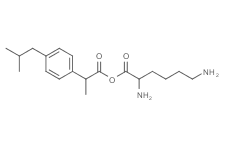
Ibuprofen Lysine
CAS No. 57469-77-9
Ibuprofen Lysine( Arflamin, Ibuprofen lysinate )
Catalog No. M18839 CAS No. 57469-77-9
Ibuprofen Lysine is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 45 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 64 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 96 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 160 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 259 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameIbuprofen Lysine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionIbuprofen Lysine is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
-
DescriptionIbuprofen lysine is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). The lysine suspension of Ibuprofen may act more quickly and effectively than base Ibuprofen.(In Vitro):Ibuprofen (24 h) inhibits COX-1 and COX-2 activity with IC50 values of 13 μM and 370 μM. Ibuprofen (500 μM, 48 h) inhibits cell proliferation and angiogenesis, and induces apoptosis in AGS cells (Adenocarcinoma gastric cell line). Ibuprofen (500 μM, 48 h) downregulates transcription of Akt, VEGF-A, PCNA, Bcl2, OCT3/4 and CD44 genes, but upregulates RNA levels of wild type P53 and Bax genes in AGS cell. Ibuprofen (500 μM, 24 h) restores microtubule reformation, microtubule-dependent intracellular cholesterol transport, and induces extension of microtubules to the cell periphery in both cystic fibrosis (CF) cell models and primary CF nasal epithelial cells. Ibuprofen (500 μM, 24 h) enhances UV-induced cell death in MCF-7 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells by a photosensitization process. (In Vivo):Ibuprofen (300 mg/kg; p.o.; daily, for 14 days) reduces overall tumor growth and enhances anti-tumor immune characteristics without adverse autoimmune reactions in a model of postpartum breast cancer. Ibuprofen (60 mg/kg; i.h.; every second day for 15 days) reduces the risk of neuropathy in a rat model of chronic Oxaliplatin induced peripheral neuropathy. Ibuprofen (20 mg/kg; p.o.; every 12 hours, 5 doses total) decreases muscle growth (average muscle fiber cross-sectional area) without affecting regulation of supraspinatus tendon adaptions to exercise. Ibuprofen (35 mg/kg; p.o.; twice daily) attenuates the Inflammatory response to pseudomonas aeruginosa in a rat model of chronic pulmonary infection.
-
In VitroIbuprofen (24 h) L-lysine inhibits COX-1 and COX-2 activity with IC50 values of 13 μM and 370 μM.Ibuprofen (500 μM, 48 h) L-lysine inhibits cell proliferation and angiogenesis, and induces apoptosis in AGS cells (Adenocarcinoma gastric cell line).Ibuprofen (500 μM, 48 h) L-lysine downregulates transcription of Akt, VEGF-A, PCNA, Bcl2, OCT3/4 and CD44 genes, but upregulates RNA levels of wild type P53 and Bax genes in AGS cell.Ibuprofen (500 μM, 24 h) L-lysine restores microtubule reformation, microtubule-dependent intracellular cholesterol transport, and induces extension of microtubules to the cell periphery in both cystic fibrosis (CF) cell models and primary CF nasal epithelial cells.Ibuprofen (500 μM, 24 h) L-lysine enhances UV-induced cell death in MCF-7 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells by a photosensitization process. Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:AGS cells Concentration:100-1000 μM Incubation Time:24 h, 48 h Result:Inhibited AGS cell viability with IC50 values of 630 μM (trypan blue staining, 24 h), 456 μM (neutral red assay, 24 h), 549 μM (trypan blue staining, 48 h) and 408 μM (neutral red assay, 48 h).
-
In VivoIbuprofen (300 mg/kg; p.o.; daily, for 14 days) L-lysine reduces overall tumor growth and enhances anti-tumor immune characteristics without adverse autoimmune reactions in a model of postpartum breast cancer.Ibuprofen (60 mg/kg; i.h.; every second day for 15 days) L-lysine reduces the risk of neuropathy in a rat model of chronic Oxaliplatin?induced peripheral neuropathy.Ibuprofen (20 mg/kg; p.o.; every 12 hours, 5 doses total) L-lysine decreases muscle growth (average muscle fiber cross-sectional area) without affecting regulation of supraspinatus tendon adaptions to exercise.Ibuprofen (35 mg/kg; p.o.; twice daily) L-lysine attenuates the Inflammatory response to pseudomonas aeruginosa in a rat model of chronic pulmonary infection. Animal Model:Syngeneic (D2A1) orthotopic Balb/c mouse model of PPBC (postpartum)Dosage:300 mg/kg, daily for 14 days Administration: Fed in animal feedings (added to pulverized standard chow and mixed dry, then mixed with water, made into chow pellets and dried thoroughly)Result:Suppresed tumor growth, reduced presence of immature monocytes and increased numbers of T cells.Enhanced Th1 associated cytokines as well as promotedtumor border accumulation of T cells.Animal Model:Oxaliplatin?induced peripheral neuropathy Dosage:60 mg/kg, every second day for 15 days Administration:Subcutaneous injection Result:Lowered sensory nerve conduction velocity (SNCV).
-
SynonymsArflamin, Ibuprofen lysinate
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetAntioxidant
-
RecptorCOX
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number57469-77-9
-
Formula Weight352.47
-
Molecular FormulaC19H32N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESNCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O.CC(C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(C)C(O)=O
-
Chemical NameL-Lysine mono(4-isobutyl-alpha-methylbenzeneacetate)
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Ferrero-Cafiero JM, et al. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Nov;53(11):972-9.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Sissotrin
Sissotrin is a natural product extracted from Pterospartum tridentatum with antimicrobial and antioxidant activities.
-
Lecanoric acid
Lecanoric acid is a compound derived from Lecanoric acid, which has antioxidant activity and promotes the growth of probiotics.
-
3’- Methoxy Puerarin
3'-Methoxypuerarin shows neuron protection activity it can protect hippocampal neurons against ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting apoptosis. 3'-Methoxypuerarin has antioxidant activities it shows ONOO(-) scavenging activity and weak NO· and O(2)(-) scavenging activities.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


